U.S. newspapers are increasing their use of co-opetition practices, that is, cooperating with competitors to reduce costs, create synergies, or reduce risk in new markets. Such activities are permissible if they are not designed to create cartels or control prices for advertising or circulation.
The latest example occurred this week when the Boston Herald announced an agreement with the Boston Globe for its competitor to print and deliver the Herald. The move creates cost savings for the Herald by allow it to cut printing, trucks, and delivery perronnel, while simultaneously creating production and distribution economies and an additional revenue stream for the Globe--a win-win for both companies.
Such service agreements do not violate antitrust laws because the papers remain independent, set their own prices, and create their own content. If papers were to engage in such actions they would have to apply for an antitrust exemption under the Newspaper Preservation Act (see John C. Busterna and Robert G. Picard, Joint Operating Agreements: The Newspaper Preservation Act and its Application. Ablex, 1993), but those agreements have not proven successful in the long run.
The Boston agreement comes on the heels of numerous printing agreements, including that of the Chicago Tribune and Chicago Sun-Times, that have been made among publishers in the last couple of years.
Another example of co-opetition is seen in the 59 newspaper and information companies—including New York Times Co., McClatchy Co., Washington Post Co., E.W. Scripps Co., A.H. Belo, and Associated Press—that have now banded together to create NewsRight to track use of digital content and ease its licensing. By cooperating with each other, the companies have brought more than 800 content sites into the operation and created a significant player in the digital industry.
Daily newspaper companies have historically disliked cooperation unless it was absolutely necessary—as in the case of news services. The new types of cooperation emerging show that the preference to go it alone is being eroded by contemporary financial conditions and the difficulties of operating independently in the digital environment.
The International Business Times is the leading provider of international business news online.
Showing posts with label New York Times Co.. Show all posts
Showing posts with label New York Times Co.. Show all posts
Newspaper Companies Start to Think Beyond Today's Bills
The somewhat improving condition of the newspaper industry is permitting companies to move from merely paying operating expenses to finding ways to improve their balance sheets and looking for new opportunities. In recent weeks:
- The Gannett Co. has placed senior notes totally $500 million that will be due in 2015 and 2018. The notes financed at 6.375% and 7.125% will give the company some financial breathing space by being used to pay a maturing loan and revolving credits. In addition it negotiated an extension on $2.7 billion in revolving credit with Bank of America from 2012 to 2014.
- The New York Times Co. has cut its debt by 40 percent in past 2 years and is beginning to look at small investments in digital media that may position it for future growth. It recently provided $4 million in financing for Ongo, a start-up news sharing site that will aggregate stories from a number of newspapers.
- The Washington Post Co. announced it would repurchase 750,000 of its outstanding shares. Such a move will increase future earnings per outstanding share and boost shareholder equity in a tax beneficial way. This type of buyback typically occurs when cash is accumulating in the company and its stock is undervalued.
PROFITS, RECESSION, AND RECOVERY
New York Times Co., Gannett Co., Media General , and McClatchy Co. have all reported profits in the second quarter and the results have led to share prices doubling and tripling.
The developments must come as a surprise to those who saw the poor performance of recent quarters and convinced themselves that the newspaper industry is dead and gone.
Admittedly, the positive results in the past 3 months were achieved through restructuring, reducing news staffs to their 1970s levels, heavy cost cutting everywhere, and postponing reinvestments. But it shows there is still life in the industry and that the industry can be expected to recover in the coming year if economic conditions continue their current rate of improvement. As I have said many times, a industry with $50 billion in revenue is not going to ignore that revenue, close the doors, and disappear overnight.
Many have viewed the poor company performance in the past 2 years and then mistaken the steep concurrent drop in advertising as evidence of a general decline caused by long-term industry trends. In doing so, they have disregarded the impact of the economy on newspaper advertising and mistaken the dramatic drop in advertising as being an indicator of the industry's broader condition rather than the shorter-term results of 4 quarters of negative growth that have affected the economy as a whole. Some have also ignored the effects of corporate debt problems had on the industry's overall condition.
In multiple blogs and articles journalists and editors have pointed out that newspapers have fared worse than other media in the recession and used that the fact as evidence that the industry is a death's door. Two decades of research on newspapers during recessions, however, has shown newspapers typically fare worse because retail and classified advertising on which the industry relies are more affected by downturns than brand advertising (See post “The Credit Crisis, Volatile Markets, and Recession and Media” and the articles below). Obviously a lot of newspaper managers and journalists don't pay attention to research about their own business.
If one looks at the newspaper advertising expenditures over time (see Figure below), one sees that they fall with recessions and then recover. This pattern was especially evident from 1991 to 1993 and 2001-2003 when short downturns pushed newspapers into decline.
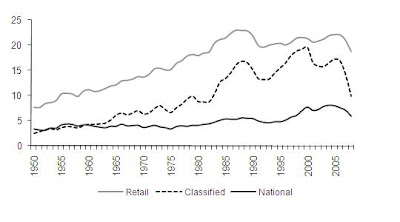
 If one considers different category of advertising, it is clear that the classified advertising—which was a driver of growth in the 1990s—was significantly troubled after 2000, but recovered and spiked in 2005 (Figure 2). Its relative decline by comparison to retail and national advertising is probably the result of some substitution with the Internet, nevertheless newspaper classifieds produced $10 billion in 2008—3 times that of online classified.
If one considers different category of advertising, it is clear that the classified advertising—which was a driver of growth in the 1990s—was significantly troubled after 2000, but recovered and spiked in 2005 (Figure 2). Its relative decline by comparison to retail and national advertising is probably the result of some substitution with the Internet, nevertheless newspaper classifieds produced $10 billion in 2008—3 times that of online classified.
 U.S. newspapers are in a mature industry with low growth potential once recovery from the recession occurs. Most companies will performance reasonably well after the recovery, but certainly some companies will have difficulties because of imprudent strategies and choices. Nevertheless, the industry as a whole will still remain in place producing revenue for many years to come.
U.S. newspapers are in a mature industry with low growth potential once recovery from the recession occurs. Most companies will performance reasonably well after the recovery, but certainly some companies will have difficulties because of imprudent strategies and choices. Nevertheless, the industry as a whole will still remain in place producing revenue for many years to come.
Picard, R.G. (2001). Effects of Recessions on Advertising Expenditures: An Exploratory Study of Economic Downturns in Nine Developed Nations, Journal of Media Economics, 14(1): 1-14.
The developments must come as a surprise to those who saw the poor performance of recent quarters and convinced themselves that the newspaper industry is dead and gone.
Admittedly, the positive results in the past 3 months were achieved through restructuring, reducing news staffs to their 1970s levels, heavy cost cutting everywhere, and postponing reinvestments. But it shows there is still life in the industry and that the industry can be expected to recover in the coming year if economic conditions continue their current rate of improvement. As I have said many times, a industry with $50 billion in revenue is not going to ignore that revenue, close the doors, and disappear overnight.
Many have viewed the poor company performance in the past 2 years and then mistaken the steep concurrent drop in advertising as evidence of a general decline caused by long-term industry trends. In doing so, they have disregarded the impact of the economy on newspaper advertising and mistaken the dramatic drop in advertising as being an indicator of the industry's broader condition rather than the shorter-term results of 4 quarters of negative growth that have affected the economy as a whole. Some have also ignored the effects of corporate debt problems had on the industry's overall condition.
In multiple blogs and articles journalists and editors have pointed out that newspapers have fared worse than other media in the recession and used that the fact as evidence that the industry is a death's door. Two decades of research on newspapers during recessions, however, has shown newspapers typically fare worse because retail and classified advertising on which the industry relies are more affected by downturns than brand advertising (See post “The Credit Crisis, Volatile Markets, and Recession and Media” and the articles below). Obviously a lot of newspaper managers and journalists don't pay attention to research about their own business.
If one looks at the newspaper advertising expenditures over time (see Figure below), one sees that they fall with recessions and then recover. This pattern was especially evident from 1991 to 1993 and 2001-2003 when short downturns pushed newspapers into decline.
 If one considers different category of advertising, it is clear that the classified advertising—which was a driver of growth in the 1990s—was significantly troubled after 2000, but recovered and spiked in 2005 (Figure 2). Its relative decline by comparison to retail and national advertising is probably the result of some substitution with the Internet, nevertheless newspaper classifieds produced $10 billion in 2008—3 times that of online classified.
If one considers different category of advertising, it is clear that the classified advertising—which was a driver of growth in the 1990s—was significantly troubled after 2000, but recovered and spiked in 2005 (Figure 2). Its relative decline by comparison to retail and national advertising is probably the result of some substitution with the Internet, nevertheless newspaper classifieds produced $10 billion in 2008—3 times that of online classified. U.S. newspapers are in a mature industry with low growth potential once recovery from the recession occurs. Most companies will performance reasonably well after the recovery, but certainly some companies will have difficulties because of imprudent strategies and choices. Nevertheless, the industry as a whole will still remain in place producing revenue for many years to come.
U.S. newspapers are in a mature industry with low growth potential once recovery from the recession occurs. Most companies will performance reasonably well after the recovery, but certainly some companies will have difficulties because of imprudent strategies and choices. Nevertheless, the industry as a whole will still remain in place producing revenue for many years to come. It will do so because more than 45 million people are still willing to purchase a paper daily and retail advertisers still gain better results from newspaper advertising than from broadcast, Internet, and other forms of advertising.
Related Articles of Interest
Picard, R.G. & Rimmer, T. (1999). Weathering a Recession: Effects of Size and Diversification on Newspaper Companies, Journal of Media Economics, 23(4):21-33.
Picard, R.G. (2001). Effects of Recessions on Advertising Expenditures: An Exploratory Study of Economic Downturns in Nine Developed Nations, Journal of Media Economics, 14(1): 1-14.
Picard, R.G. (2008). “Shifts in Newspaper Advertising Expenditures and their Implications for the Future of Newspapers,” Journalism Studies, 9(5):704-716.
van der Wurff, R., Bakker, P. & Picard, R.G. (2008). Economic Growth and Advertising Expenditures in Different Media in Different Countries, Journal of Media Economics, 21:28-52.
3 BIG FAMILY OWNED MEDIA FIRMS FACE SIGNIFICANT CHALLENGES
Family owned and controlled businesses face challenges because of difficulties in passing firms on to succeeding generations of the family. Tax issues are a common problem, but the biggest challenges involve finding effective managers among the family and the needs for new capital that diminishes family control.
How family members view the company over time create problems for sustainability. Individuals who establish firms tend to view it as a business enterprise; their children tend to see it as supporting the family; and multigenerational family businesses tend see it has providing status in the community. These latter priorities can interfere with profit and reinvestment objectives and endanger long-term sustainability.
As a consequence of these kinds of factors, only about 30% of family firms are passed to a second generation and only 13% reach a third generation.
This brings us to the challenges facing media firms. Three big companies—News Corp., Viacom, and New York Times Co.— all are struggling with succession and control issues.
Rupert Murdoch, who built the News Corp. global empire after inheriting the firm from his father, is now 77 and having difficultly convincing an heir to take over. The oldest son, Lachlan, left the company three years ago and his other children, James and Elizabeth, recently declined to become his number 2. James still runs the company’s European and Asian operations, but Elizabeth prefers to run her own independent TV production company. Whether the company can remain family run in the coming years is unclear.
Sumner Redstone—who is 75 and has had strategic disagreements with many managers at Viacom—turned to his daughter Shari Redstone to help manage National Amusements, Viacom and CBS. She proved quite adept and by 2005 it was assumed that she would succeed Sumner as head of the company. The two had a serious falling out two years ago over succession and governance, however, and it is now uncertain who will lead the firm in the future. Certainly it won’t be Sumner’s son Brent, who sued him over disputes about his portion of the family business.
The Sulzberger family is struggling to maintain control over the strategic direction and operation of New York Times Co., despite the greater influence they have because of that companies preferential share structure. They increasingly have to go outside the company for capital—such as making the deal with Mexican mogul Carlos Slim—and they are continuing struggling with other major investors who are demanding more influence on company management. The family is slowly losing the automony it once had in running the company.
If solutions to succession and family control issues are not found, it is likely that these firms may have to turn to outside managers. History has show that when that occurs, family members become detached from the firm and are more likely to sell their shares and leave the business altogether.
How family members view the company over time create problems for sustainability. Individuals who establish firms tend to view it as a business enterprise; their children tend to see it as supporting the family; and multigenerational family businesses tend see it has providing status in the community. These latter priorities can interfere with profit and reinvestment objectives and endanger long-term sustainability.
As a consequence of these kinds of factors, only about 30% of family firms are passed to a second generation and only 13% reach a third generation.
This brings us to the challenges facing media firms. Three big companies—News Corp., Viacom, and New York Times Co.— all are struggling with succession and control issues.
Rupert Murdoch, who built the News Corp. global empire after inheriting the firm from his father, is now 77 and having difficultly convincing an heir to take over. The oldest son, Lachlan, left the company three years ago and his other children, James and Elizabeth, recently declined to become his number 2. James still runs the company’s European and Asian operations, but Elizabeth prefers to run her own independent TV production company. Whether the company can remain family run in the coming years is unclear.
Sumner Redstone—who is 75 and has had strategic disagreements with many managers at Viacom—turned to his daughter Shari Redstone to help manage National Amusements, Viacom and CBS. She proved quite adept and by 2005 it was assumed that she would succeed Sumner as head of the company. The two had a serious falling out two years ago over succession and governance, however, and it is now uncertain who will lead the firm in the future. Certainly it won’t be Sumner’s son Brent, who sued him over disputes about his portion of the family business.
The Sulzberger family is struggling to maintain control over the strategic direction and operation of New York Times Co., despite the greater influence they have because of that companies preferential share structure. They increasingly have to go outside the company for capital—such as making the deal with Mexican mogul Carlos Slim—and they are continuing struggling with other major investors who are demanding more influence on company management. The family is slowly losing the automony it once had in running the company.
If solutions to succession and family control issues are not found, it is likely that these firms may have to turn to outside managers. History has show that when that occurs, family members become detached from the firm and are more likely to sell their shares and leave the business altogether.
NEWSPAPER RESTRUCTURING IS PAINFUL, BUT NECESSARY
Financial pages are full of developments and changes at newspaper companies and these are being commented upon anxiously by those in the industry. Unpleasant conditions certainly abound, but these development are not indications that the industry is dead or dying in the near future. What they signal is that things which worked in the past are not working now, that newspaper companies are badly in need of restructuring, refocusing, and renewal, and that the boards of the companies and the company managers are taking badly needed action.
The techniques for restructuring are no mystery. First, you need some cash. This can be obtained by attracting new capital through investment or loans. New York Times Co. did this recently by borrowings $250 million from Carlos Slim. Other firms are looking for friendly investors with liquidity.
Another way of raising cash is by turning assets into cash. A classic move made by many types of firms is the sell their building and lease back any space that is needed. Media General and New York Times Co. are currently employing this tactic. Financially troubled companies can also be expected to shed some of their poorest or best performing holdings to raise cash, so it is likely that we will see a number of newspapers companies putting papers up for sale in the near future.
Reducing and restructuring existing debt lessens financial performance pressures on companies. To accomplish it, they use cash that is raised to pay obligations imminently due or to make early partial payments to debt holders in exchange for obtaining better interest rates or lengthening payment terms. Watch for such transactions in the coming months.
As part of restructuring, many newspaper-based companies will seek to refocus on core news and informational activities, divesting non-core activities to raise cash. Baseball teams, holdings in cable systems, advertising service firms, and other types of peripheral companies are being sold or considered for sale.
Few newspaper company executives have experience restructuring and reorganizing their firms to make them leaner and more efficient or strong financial management background. The current environment requires different managerial skills so many newspaper firms will be looking outside the industry for experience. GateHouse Media, for example, has now hired a chief financial officer with a financial management background at companies including PayCheck, NCR , and PriceWaterhouse.
Expect to see multiple actions throughout the industry that are parts of the restructuring of newspaper companies in the coming month. Some will be painful, but will have two effects. First, it will lessen the financial pressures of the debt many companies are carrying. Second, it will force them to rethink their newspapers and the value and quality they are or aren’t providing.
The techniques for restructuring are no mystery. First, you need some cash. This can be obtained by attracting new capital through investment or loans. New York Times Co. did this recently by borrowings $250 million from Carlos Slim. Other firms are looking for friendly investors with liquidity.
Another way of raising cash is by turning assets into cash. A classic move made by many types of firms is the sell their building and lease back any space that is needed. Media General and New York Times Co. are currently employing this tactic. Financially troubled companies can also be expected to shed some of their poorest or best performing holdings to raise cash, so it is likely that we will see a number of newspapers companies putting papers up for sale in the near future.
Reducing and restructuring existing debt lessens financial performance pressures on companies. To accomplish it, they use cash that is raised to pay obligations imminently due or to make early partial payments to debt holders in exchange for obtaining better interest rates or lengthening payment terms. Watch for such transactions in the coming months.
As part of restructuring, many newspaper-based companies will seek to refocus on core news and informational activities, divesting non-core activities to raise cash. Baseball teams, holdings in cable systems, advertising service firms, and other types of peripheral companies are being sold or considered for sale.
Few newspaper company executives have experience restructuring and reorganizing their firms to make them leaner and more efficient or strong financial management background. The current environment requires different managerial skills so many newspaper firms will be looking outside the industry for experience. GateHouse Media, for example, has now hired a chief financial officer with a financial management background at companies including PayCheck, NCR , and PriceWaterhouse.
Expect to see multiple actions throughout the industry that are parts of the restructuring of newspaper companies in the coming month. Some will be painful, but will have two effects. First, it will lessen the financial pressures of the debt many companies are carrying. Second, it will force them to rethink their newspapers and the value and quality they are or aren’t providing.
THE UPSIDE OF DISAPPEARING NEWSPAPER ADVERTISING
There is one upside to all the advertising disappearing from newspapers……Consumers can now really see what they are paying for.
Opps, that’s a BIG downside.
With the effects of economic downturn clearly hitting retailers everywhere, they have slashed their advertising budgets and are advertising as little as possible. For the first time in my lifetime it means you can turn several pages in many newspapers without seeing an advertisement. When I read the Boston Globe on Tuesday (January 7), it essentially had 2 pages of ads in the 10-page A section, 3 pages of ads in the 16-page B section, and 1 page in the 8-page C section. It had no ads on page 1 (although it has been announced they will start doing so soon) and the daily classified section is no longer being published on weekdays. What was left was editorial content. Unfortunately, what was there wasn’t pretty.
In reading the paper I realized that about half the stories were from news agencies and services and that I had read many of them day before on Yahoo! News and the New York Times and Washington Post websites. A number of the paper’s local stories were on the Boston.com site or other Boston sites before they appeared in print. I am an avid news consumer and love the paper format, but the paucity of original and novel content left me wonder “Why am I still paying for the paper, especially when I have to call at least once a week because of delivery problems.”
I single out the Globe here, but the problem is everywhere I look at newspapers.
Publishers and editors just don’t get it. They have to stop pining that the old days were better and they have to stop blaming everything and everyone but themselves for the lack of value in their papers. What readers need—if they are going to keep buying papers—is content and an experience with news that they cannot get elsewhere. It has to be BETTER than that on TV, Internet, and mobile applications; it has to DIFFERENT than what they get from those sources; and it has to be news for those who LOVE news.
If editors and publishers don’t start delivering those qualities, they will soon have to stop delivering papers altogether.
Opps, that’s a BIG downside.
With the effects of economic downturn clearly hitting retailers everywhere, they have slashed their advertising budgets and are advertising as little as possible. For the first time in my lifetime it means you can turn several pages in many newspapers without seeing an advertisement. When I read the Boston Globe on Tuesday (January 7), it essentially had 2 pages of ads in the 10-page A section, 3 pages of ads in the 16-page B section, and 1 page in the 8-page C section. It had no ads on page 1 (although it has been announced they will start doing so soon) and the daily classified section is no longer being published on weekdays. What was left was editorial content. Unfortunately, what was there wasn’t pretty.
In reading the paper I realized that about half the stories were from news agencies and services and that I had read many of them day before on Yahoo! News and the New York Times and Washington Post websites. A number of the paper’s local stories were on the Boston.com site or other Boston sites before they appeared in print. I am an avid news consumer and love the paper format, but the paucity of original and novel content left me wonder “Why am I still paying for the paper, especially when I have to call at least once a week because of delivery problems.”
I single out the Globe here, but the problem is everywhere I look at newspapers.
Publishers and editors just don’t get it. They have to stop pining that the old days were better and they have to stop blaming everything and everyone but themselves for the lack of value in their papers. What readers need—if they are going to keep buying papers—is content and an experience with news that they cannot get elsewhere. It has to be BETTER than that on TV, Internet, and mobile applications; it has to DIFFERENT than what they get from those sources; and it has to be news for those who LOVE news.
If editors and publishers don’t start delivering those qualities, they will soon have to stop delivering papers altogether.
MEDIA FIRMS INCREASINGLY CHARGED WITH COPYRIGHT VIOLATIONS
First it was record companies suing Napster and peer-to-peer file sharers, and then it was media companies such as Viacom, Universal Music Group, and Agence France Presse suiting Google, YouTube, and Facebook for distributing content whose rights they owned. Now GateHouse Media has filed suit against another newspaper firm, the New York Times Co., for publishing content from its websites and papers on Boston.com.
That media companies are suing each other is a sure sign of the maturation of online distribution and that money is starting to flow—albeit slowly and at levels far below that of traditional media, which still account for more than two-thirds of all consumer and advertiser expenditures
But the lawsuits really point out the weakness of revenue distribution for use of intellectual property online. In publishing, well-developed systems for trading rights and collecting payments exist. In radio, systems for tracking songs played and ensuring artists, composers, arrangers, and music publishers are compensated are in place and working well. The trading of rights for television broadcasts and mechanisms for payments to owners of the IPRs are well established.
However, effective systems are absent in online distribution and the industry needs to move rapidly to establish them. If the industry can not create such a system on their own, more money will go to lawyers and the rules and systems for online payments will ultimately be imposed by courts or legislators who tire of the governmental costs for solving disputes and enforcing the rights.
Organizations representing print and audio-visual media need to sit down with their major counterparts in online distribution to create a reasonable mechanism by which rights are traded and revenues shared, otherwise they risk imposition of a government imposed compulsory license scheme that will be less desirable to the industry.
Companies that continually argue there should be less government regulation of media operations can’t increasingly go to government to solve their disputes without expecting it to produce more regulation.
That media companies are suing each other is a sure sign of the maturation of online distribution and that money is starting to flow—albeit slowly and at levels far below that of traditional media, which still account for more than two-thirds of all consumer and advertiser expenditures
But the lawsuits really point out the weakness of revenue distribution for use of intellectual property online. In publishing, well-developed systems for trading rights and collecting payments exist. In radio, systems for tracking songs played and ensuring artists, composers, arrangers, and music publishers are compensated are in place and working well. The trading of rights for television broadcasts and mechanisms for payments to owners of the IPRs are well established.
However, effective systems are absent in online distribution and the industry needs to move rapidly to establish them. If the industry can not create such a system on their own, more money will go to lawyers and the rules and systems for online payments will ultimately be imposed by courts or legislators who tire of the governmental costs for solving disputes and enforcing the rights.
Organizations representing print and audio-visual media need to sit down with their major counterparts in online distribution to create a reasonable mechanism by which rights are traded and revenues shared, otherwise they risk imposition of a government imposed compulsory license scheme that will be less desirable to the industry.
Companies that continually argue there should be less government regulation of media operations can’t increasingly go to government to solve their disputes without expecting it to produce more regulation.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)