The International Business Times is the leading provider of international business news online.
THE WIDENING RANGE OF REVENUE SOURCES IN NEWS ENTERPRISES
The financial uncertainty facing the industry is not unusual, however. We tend to forget that news has historically been unable to pay for itself and was subsidized by other activities. In the past newspapers and other news organizations engaged in a far larger range of commercial activities than then they do today and publishers had to be highly entrepreneurial and seek income from a wide variety of sources in order to survive.
The initial gathering and distribution of news was paid for by emperors, monarchs, and other rulers who needed information for state purposes. Later, wealthy international merchants hired correspondents to gather and relay news that might affect their businesses. When news became a commercial product, newspaper publishers subsidized the operations with profits from printing books, magazines, pamphlets, and advertising sheets, income for editors from shipping and postal employment, profits from operating book shops and travel agencies, and subsidies from communities and political and social organizations.
Today, however, news organizations are struggling to maintain themselves and develop digital operations by primarily focusing on the two revenue streams they have known in recent decades: subscriptions and advertising. Many people are being disappointed because those are failing to provide sufficient financial resources to sustain their operations.
The need to seek income from multiple sources is clear, but runs somewhat counter to the values of twentieth-century professional journalism, which denigrates commercial activity and thus engenders organizational resistance to new business initiatives. Continuing staff reductions and other budgetary cutbacks are eroding some internal opposition, but are rightfully leading to questions about how far one goes down the commercial road before news gives up its independence.
In both the online and offline news worlds, a wide variety of revenue generating activities are appearing—some based on traditional subscriber/single copy sales and advertising sales—but many others moving into new areas of monetization.
Many news organizations are increasing the range of advertising services provided to sell and create ads for their own media products, but also to provide clients services that can be used in competing products as well. New types of advertising offerings are being created to link across platforms, sponsorships of online and mobile news headlines are developing, video advertising is being offered online, and special “deals of the day” advertising spots are being offered.
Some organizations are increasing their product lines producing paid premium products and niche content for professional groups and persons with special interests; some are providing business service listings for a fee; others are creating a variety of non-news products; still others are operating additional business units creating paid events, running cafés, book and magazine shops, and providing training and education activities.
Sales of other products and services are being increasingly embraced through e-commerce (linking published reviews films, performances, and recordings to sites where customers can buy tickets, DVDs, CDs, etc.), creating and selling lists and databases of local businesses and consumers, producing special reports and books, selling photographs and photography services, and even selling items such as computers and appliances.
A growing number of news organizations are seekings subsidies though reader memberships and donations and grants from community and national foundations.
These are healthy developments because they increase the opportunities to create revenue that can fund news activities. Obviously, the abilities and willingness of different news enterprises to engage in the range activities vary widely, but the fact that they are appearing show that news organizations are beginning to adjust to the new environment and becoming more entrepreneurial than they have been for many decades.
What is needed now is not knee-jerk opposition to these efforts from news personnel, but thoughtful development of realistic principles and processes to minimize any negative effects of these new initiatives on news content so that trust and credibility are not diminished.
IMPLICATIONS OF CHANGING DEFINITIONS OF MEDIA MARKETS
Newspapers are becoming news providers, delivering news and information via print, online, mobile, and other platforms; broadcasters are moving off the radio spectrum, exploiting not only other streaming and video-on-demand opportunities, but also text-based communication on web and mobile platforms.
Although functional definitions clarify what companies actually do, they obscure wide differences in audiences, business relations, and revenue sources on the different platforms and give some the mistaken impression that a functionally defined operation can be successful operating the same way across the different platform environments. The functional definition is also confusing some policy makers and regulators concerned with effects of cross-media activity, consolidation, and concentration who do not carefully sort out the different elements of product and geographic market definitions among the platforms.
From the business standpoint, the fundamental problem of the functional definitions is that it leads many content providers to believe they can simply repurpose existing content across platforms. They are happy to do so because the marginal cost is near zero, but they ignore the facts that it also commoditizes the content, that the content losses uniqueness, and that similar presentation may not be appropriate on other platforms. Consequently, the repurposed content can produce only a small marginal increase in revenue.
To ultimately be successful in functional markets, companies need to offer a good deal of new content and launch new products on the new platforms rather than merely reusing what is already there in the traditional ways. Leading cable channels, for example, early in their development relied on motion pictures and syndicated programs previously shown on network television, but soon realized that they needed original programming to attract better audiences and gain additional revenue. Financial newspapers have begun to get it right on the Internet, offering more content and tools than in their print editions and establishing specialized niche products for different types of industry and business readers.
We are all watching to see who among general content providers manages to get their functional approach to markets right using the Internet, Mobile, e-Readers, and other platforms.
MEDIA, INNOVATION, AND THE STATE
State support for innovation is not a new concept. Support of cooperate research initiatives involving the state, higher education institutions, and industries has been part of national science and industrial policies for many decades. There has been significant state support for innovation of agriculture/food products, electronics, advanced military equipment, information technology, and biomedical technology and products.
State support tends to work best in developing new technologies and industries and tends to focus support on advanced basic scholarly research through science and research funding organizations, creation and support for research parks and industrial development zones for applied research, and incentives and subsidies for commercial research and development.
Many governments also support efforts to transform established industries. These are typically designed to promote productivity and competitiveness as a means of preserving employment and the tax base. In the past there has been some support for technology transfer from electronics and information technology to existing industries and for retraining, facilities reconstruction, and entering new markets.
Trying to apply those kinds of research and transformation policies in media is challenging, however, because much of media activities tend to be non-industrial and are dependent on relatively rigid organizational structures and processes that are difficult to change. These factors are complicated by the facts that media engage in negligible research and development activities, have limited experience with product change and new product development, and tend to have limited links to higher education institutions.
It is clear that a growing number of managers in media industries understand the need for innovation because of the declining sustainability of current operations and because Internet, mobile, e-reader, and on-demand technologies are providing new opportunities. The real innovation challenges in established media, however, are not perceiving the need for change or being able to get needed technology, but organizational structures, processes, culture, and ways of thinking that limit willingness and ability to innovate. This is compounded because many managers are confused by the opportunities and don’t know what to do or how pursue innovation.
Today, the innovation challenge facing media—especially newspapers--is not mere modernization, but fundamentally reestablishing their media functions and forms. What is needed is a complete rethinking of what content is offered, where, when and how it is provided, what new products and services should be provided and what existing ones dropped, how content will differ and be superior to that of other providers, how to establish new and better relationships with consumers, how the activities are organized and what processes will be employed, what relationships need to be established with partners and intermediaries, and ultimately how the activities are funded.
The state’s ability to influence media innovation of this type is highly constrained. Governments worldwide have proven themselves ineffectual in running business enterprises and they have limited abilities to affect organizational structures, processes, culture, and thinking in existing firms. What governments can do, however, is to fund research that identifies threats, opportunities and best practices, provide education and training to promote innovation and help implement change, offer incentives or subsidies to cover transformation costs and support new initiatives, and help coordinate activities across industries.
These kinds of support will be helpful, but they will not be a panacea because the greatest impetus for and implementation of change and innovation must come from within companies. The support will only be helpful if companies are actually willing to innovate and change to support that innovation. The extent they are willing to do so remains to be seen.
FAIL OFTEN. FAIL EARLY. FAIL CHEAP.
Managers who have been used to stable environments and well conceived plans are often reticent to move to seize opportunities with quick and decisive action based on incomplete information and knowledge. The turbulent contemporary environment, however, require leaders to rapidly evaluate the potential of new communication opportunities and to take risks in a highly uncertain setting.
This is disturbing to managers who are used to employing well developed and elegant strategies that require significant investment and commitment. Declining to test opportunities until a clear roadmap is produced, however, takes away flexibility and the ability to rapidly change with contemporary developments.
While preserving the core activities of media businesses, managers need to simultaneously look for emerging opportunities that can be pursued, communities that can been served, and experiences that can be delivered. It is important to get in quick and inexpensively, to build on small successes, and to abandon initiatives if success proves elusive.
It is better to fail often, fail early, and fail cheap than to avoid risky moves, lose potentially rewarding opportunities, and forgo learning from innovative initiatives.
In the current tumultuous environment, failure has become a form of research and development. Try things; drop those that don't take you somewhere interesting; document what you learn from each unsuccessful initiative; move on to something new. What you learn from unsuccessful efforts is usually more important that what you from success.
The only real failure in the rapidly changing world of media is doing nothing and hoping things will get better on their own,
JOURNALISM AS CHARITY AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP
The latest group to do so is former Rocky Mountain News reporters who started rockymountainindependent.com this past summer using a membership payment and advertising model. The effort collapsed Oct. 4 with them telling readers, “We put everything into producing content and supporting our independent partners, but we can no longer afford to produce enough content to justify the membership.”
There problem is hardly unique. The conundrum facing many journalists is whether to pursue the noble work of journalism as unpaid charitable work or to become engaged as journalistic entrepreneurs with a serious attitude toward its business issues—something many despised in their former employers.
If journalists want pay for their work, if they want to provide for their families, and if they want to pay mortgages, they need to spend more time figuring out how to provide value that will extract payments from readers and advertisers. To do that they have to construct organizational structures and activities that support the journalism; they will have to ensure that startups have sufficient capital; and they will have to engage staffs in marketing and advertising activities, not merely news provision.
One of the most difficult issue for these new journalism providers—as well as existing print and broadcast providers—is that journalists tend to overestimate the value of news for the public. What the public actually wants is less, not more, news.
It is not that the public doesn’t want to be informed, however. It is just that journalists spend so much time, space, and effort conveying commodity news that provides little new and helpful information for readers and cannot generate sufficient financial support. By commodity news I mean the simplistic who, what, and where stories about what happened yesterday. Those kinds of stories are readily available from many sources and provides readers little for which they will pay.
Instead, in a world of ubiquitous commodity journalism, successful journalists need to be spending time exploring the how and why of events and issues and helping readers understand and cope with what is expected next. Effective journalism in the new environment needs to focus more on today and tomorrow than on yesterday.
Success in the contemporary journalism environment it is not merely about providing news, but about providing helpful and advisory news explanation based on solid values and identity to which readers can relate. It must be part of entrepreneurial journalism or new ventures will fail.
To get there, however, journalists starting up new enterprises will need to develop resources and entrepreneurial motivation to sustain their efforts more than a few months. Most new commercial and noncommercial enterprises require 18 to 36 months of operation before they develop a loyal audience and achieve a stable financial situation. Unless journalists are willing to work for free during that time, they will have to raise capital to survive; and if they want their new organizations to thrive and develop they will have to provide a different kind of news than most are used to creating. It will need to be unique and better than what is already available.
4 STRATEGIC PRINCIPLES FOR EVERY DIGITAL PUBLISHER
This occurs because publishers become focused on issues of content delivery and uncritically accept the fundamental elements of the processes involving platforms and intermediaries. In order to gain the fullest future benefits from the digital environment, however, publishers needs to strategically consider and direct activities involving the users, advertisers, prices, and purposes of their new platforms.
In creating business arrangements with platform and service providers and intermediaries, 4 fundamental strategic principles should guide your actions:
1. Control your customer lists. The most important thing you do as a publisher is to create relationships with and experiences for your customers. It is crucial to ensure that your content distribution and retail systems do not separate you from those who read, view, or listen to your content. If you do not operate your distribution or pay systems, or don’t have strong influence over their operations, this important part of the customer experience falls outside your control and— worse—you never establish direct relationships with customers that allow you to get to know them better, to create stronger bonds, to use them to improve your products, or to up-sell services. If you must use intermediaries, ensure that you have full access and rights to use e-mail, mobile, and other addresses for all your content customers and that you have some influence over the look, feel, and content of the contacts that your service providers have with your customers.
2. Control advertising in your digital space. Users see advertising placed on your website, your mobile messages, and your e-reader content as part of your product and it affects the experience you deliver to them. It is not enough to control the size and placement of ads; you also need to control the dynamic functionality, types, and content of ads. The experience your product delivers is of little interest to outside providers of digitally delivered advertising, but it must be to you. You should control your own advertising inventory and maintain approval rights and—as with audiences—you should have the ability to make direct contact with advertising customers so you can add value by working with them to achieve greater effectiveness and provide better benefits across your content platforms.
3. Control your own pricing. Do not put yourself in the position of merely accepting the ad suppliers’ price and payment for advertising appearing in your digital product. The digital space and audience contact that you provide is the product and service being purchased and some contact is more valuable than others. Know how your value compares to that of competitors and set your prices according. Don’t be a price taker, be a price maker. Digital advertising will not grow to become an important part of your business if you let the most important decision of the revenue model reside in someone who does not care about your business.
4. Drive customers to platforms most beneficial to you. Digital media give you the opportunities to serve customers where and when they want to be served, but you need to use those opportunities to drive them to your financially most important product. Internet sites, e-readers, mobile applications, and social media are highly useful for contact and interaction, but not yet very effective for revenue generation. The best effects typically result from increasing use of your offline product or driving traffic to your most finally effective digital location. Make sure that all the distribution platforms you use are configured for easy movement to other digital platforms that benefit you most, even if they don’t directly benefit your service provider.
Digital publishing can only become successful if you get the business fundamentals correct by controlling the most important commercial aspects of the operation. The value configuration created by customer interfaces and partner networks must be arranged to work in your favor and strategic thinking needs to guide how you organize and direct those activities.
CAN PUBLIC BROADCASTERS HARM COMPETITION AND DIVERSITY?
The Federal Communications Commission will have to consider that question shortly when it considers the effort of WGBH Education Foundation—operator of WGBH-TV, the highly successful Boston-based public service broadcaster—to purchase the commercial radio station WCRB-FM.
WGBH is the top ranked member of the Public Broadcasting Service in the New England and produces about one third of PBS’ programming. It operates a second Boston television station, WGBX-TV, and WGBY in Springfield, Massachusetts. In addition it operates FM radio stations WGBH (Boston), WCAI (Woods Hole), WZAI (Brewster), and WNAN (Nantucket) and is a member of National Public Radio and Public Radio International. It operates two commercial subsidiaries involved in music rights and motion picture production.
This month it announced it was planning to purchase WCRB-FM, a classical music station that serves the Boston area. The purchase would allow it to alter its WGBH-FM format to compete more directly with WBUR-FM, the leading public radio station in Boston that is operated by Boston University.
WGBH Educational Foundation is an enterprise with $580 million in assets and revenues of $280 million annually. It has more than 600 employees who are paid more than $50,000 annually and has 5 paid more than $225,000. Its president and CEO is paid about $340,000 and 2 vice presidents about $250,000 annually. This is not a small, poor charitable enterprise.
Were WGBH a commercial broadcaster, those who hate big media would be howling in protest, arguing that it puts far too much control of the airwave in the hands of one organization and that the concentration will create market power that harms competition. But they are strangely silent.
However, in deciding whether to permit the purchase, the FCC will have to consider whether the expansion of the public broadcaster harms competitors and plurality and diversity.
Similar questions are being asked elsewhere as well. Across the pond, the British Broadcasting Corp. has recently been the target of a good deal of criticism because of its increasingly commercialized operations and because its expansion of public service operations in TV, Radio, and Internet at the local, national, and international level are seen as affecting commercial firms and competition.
The BBC is one of the largest broadcasting companies in the world, operating on revenues of £4.7 billon ($7.4 billion) and it has assets of £1.5 billion ($2.4 billion).
Many commercial broadcasters and publishers in the U.K. have criticized the growth of the BBC operations and the debate became especially heated recently when James Murdoch, the News Corp. head in Europe and Asia, made a public speech charging the BBC was engaging in a “land grab” and that its ambitions were “chilling.”
“The expansion of state-sponsored journalism is a threat to the plurality and independence of news provision, which are so important for our democracy," Murdoch told the Edinburgh International Television Festival. Whether you agree with him or not, you have to give him credit for co-opting the language of critics of big commercial media.
News Corp. and the other commercial firms competing with the BBC obviously have self interests at heart, and some commercial firms have certainly behaved in ways that harmed public interests in the past, but their arguments should not be casually dismissed.
If competition among commercial firms, between commercial and non-commercial firms, and among non-commercial firms is good for pluralism and diversity, cannot concentration and reductions in sources of news and entertainment due to acts of large not-for-profit firms also harm competition, pluralism and diversity?
Import Export Business Answers
message: I have a family member that is living in Jamaica. We are trying to find out the laws of me buying stuff here in the US and shipping them to Jamaica where she can sell out of a store. I just need help finding out if i need a license and if so what type. Are you able to help me with this question? Please let me know.
Answer:
You are asking a question that could have many potential
answers.
Most of the time, there are no licenses required to ship
something from country to country unless it is considered
hazardous like chemicals, weapons, etc..
If you are talking about large, container size shipments, then
you should talk with a freight forwarder to assist you. If you are
talking about boxes that can be shipped via the post office, you
can talk to someone at a reasonably sized post office.
If it is small enough to ship via the post office, it will most likely
be the cheaper way to both ship and get through customs. See
many times there are no restrictions or fees other than shipping
from the country a product ships from but there are fees (customs,
duties, etc) that are due by the buyer upon receipt.
You may also find some information posted at the US Postal web site at www.USPS.com - there is usually a customs form
you have to complete at the Post office showing what is in th e
package and the estimated value (this is how the receiving
country ends up taxing or charging customs).
As an example, we used to sell an automotive product on our
web site and in Canada, they charged about $25 on a $150 valued
item which was about 16 to 17% of the items value.
Fresh food items often require special handling due to bugs,
spoilage, etc..
Hope this will help get you pointed in the right direction.
Ron Coble
International Business Services
PUBLISHERS URGE MORE PUBLIC AID FOR NEWSPAPERS, BUT H.R. 3602 WON'T SOLVE THEIR PROBLEMS
This is a case of the newspaper industry seeking long-term business benefits to solve a short-term crisis caused by poor management decisions and the recession. The leading newspaper firms and their representatives are making concerted efforts to dupe legislators and the public into believing their troubles are part of the general trends in the industry, rather than the result of management decisions and the financial crisis that is diminishing. If the provisions are passed, the public treasury will be diminished for years to come and risks for employee pensions will be increased.
Newspaper executives and other witnesses were sympathetically treated at the hearing this week, but it is unclear whether they will be able to achieve the policies they advocated.
Another proposal that the commercial firms are uninterested in themselves, but expressed sympathy for, would broadening laws regarding charities to include not-for-profit newspapers. Their support was astute because the House Joint Economic Committee’s chair, Rep. Carolyn Maloney (D-NY), has introduced her own bill (H.R. 3602) to allow newspapers to become tax exempt under section 501(C)(3) of the tax code. Her bill somewhat mirror Senate bill 673 by Sen. Benjamin Cardin, D-Md., that was discussed earlier in this blog (Analysis of the Newspaper Revitalization Act, http://themediabusiness.blogspot.com/2009/03/analysis-of-newspaper-revitalization.html). There are some differences in Maloney’s bill that need to be highlighted.
Under Section (b) of H.R. 3602, companies would qualify for tax exempt status through a 3-part test.
First, companies would have to be “publishing on a regular basis a newspaper of general circulation” to qualify. This provision stipulates no periodicity so it does not limit qualification to dailies, which are experiencing the greatest economic and financial difficulties. This language provides the exemption only to established papers and would thus exclude startups until after they were regularly publishing, requiring startups to initially obtain financing through other than tax-deductible donations.
The language in this first test requires that publications be “a newspaper of general circulation” and this will lead to questions whether it applies to newspapers focused on specific audiences in a community—such as African Americans or senior citizens—or papers providing more focused content—such as news and information for a specific neighborhood or devoted solely to politics or crime. This ambiguity could be used by IRS examiners against some papers and could be used by some publishers to take advantage of a policy not intended for them.
The second provision requires that qualifying papers publish “local, national or international stories of interest to the general public and the distribution of such newspaper is necessary or valuable in achieving an educational purpose.” The provision regarding type of coverage is better than the Senate bill because it does not require publication of all 3 types of news—something not done in many local papers.
The third provision requires that content preparation “follows methods generally accepted as educational in character.” This provision is exceedingly vague and its application is unclear because it does not deal with the content of the paper, but with the preparation of the paper. How “the preparation of the material” follows accepted educational methods would seem to require that the papers be part of an educational activity, such as being linked to training in schools or universities. This would highly limit the applicability of the bill to existing newspaper operations.
Like the Senate bill, Section (c) permits papers to carry advertising “to the extent that such newspaper does not exceed the space allotted to fulfilling the educational purposes of such qualified newspaper corporation.” This would require papers to publish no more than an equal amount of editorial and advertising content. This is lower than the limit of postal service limit (75%) and would force most existing papers to drop about 1/3 of their existing advertising or incur damaging costs by printing more news pages than they do now. This would cripple the finances of any daily paper.
Finally, Section (d) of the legislation permits qualified companies to accept tax deductable charitable donations to support their operations.
This bill, like its Senate predecessor, is likely to have limited affects on the newspaper industry because it will not interest newspaper owners because most of their papers are producing profits and it will preclude their abilities to benefit from greater profits when the advertising recovery occurs.
There is a place for not-for-profit media and journalism, but H.R. 3602 S. 673 will not do much to improve coverage or the overall condition newspaper industry. It is likely to continue to gain support from the commercial newspaper industry, however, because it can be used to provide cover for government policies that they really want.
How To Price A Product
You must get the price right... the first time because in the digital marketplace, there are very few second chances. "Make Your Price Sell!, The Masters Course" helps you turn your website visitors into pricing experts.
This FREE course provides your website visitors with the strategies and info they need to determine the "Perfect Price." This course details background pricing theory, profiling target markets, key business models and the importance of a product or services perceived value, and much more.
These factors represent the big picture for your visitors to consider. The perfect price is most important when you are actually at the point of selling and monetization is merely the 4th of the four-step CTPM process. Here is a break down of the ultimate online success equation...
Right Processes + Great Products(or Services) + Perfect Price = Customer Satisfaction
You may download your FREE "Make Your Price Sell - Masters Course" by clicking on this link.
RADIO STATIONS FACE SIGNIFICANT STRATEGIC CHALLENGES
The challenges are being caused by declining demand for radio offerings due to lifestyle changes, the wide availability of substitutable audio platforms, and the primary content currently being offered. Audience behavior toward radio is changing and many U.S. stations now only make money for 4 to 6 hours each day. Overall, audiences are spending less time with radio and exhibiting less station loyalty than they did in the past, and young audiences are particularly difficult to attract and serve.
A major impetus of change is that audiences for music worldwide are progressively replacing radio listening with personalized playlists they have created on their computers, MP3 players, and mobile phones and by CDs on which they burned those favorites. They select music that suits their individual tastes and many have wider repositories of music in their own libraries than are offered on broadcaster playlists. Satellite and Internet radio are compounding the problem by offering hundreds of choices of highly focused music formats. These developments are increasingly making radio a less relevant platform for music entertainment delivery than it has been.
Concurrently, a wide variety of non-music programming is being offered by Satellite and Internet stations and audiences are increasingly using these services, as well as downloading podcasts on a variety of topics of individual interest from both broadcast and non-radio sources.
These problems are compounded in the U.S. because the rise of radio groups after deregulation in the mid 1990s led to national radio programmers making selections, reducing the range of genres of music and other content on radio stations. Overall, programming has become less local and less relevant as content decisions have been made elsewhere.
Advertisers sense the problem with audiences and the share of advertising expenditures going to radio is declining. Worldwide radio advertising expenditures are about 7 percent of total expenditures, down from a height of 9 percent in 1999. In the U.S. they peaked in 2002 at nearly 13 percent and are now down to about 10 percent. This downward trend is seen among most of the traditional leaders in radio advertising expenditures –Mexico, Japan, France, UK, Spain—and only in rapidly developing countries such as Brazil and China is the share spent on radio on a clear upward trajectory.
Another indicator of the problem is seen in the considerable weakening of sales prices for radio stations in recent years.
Radio station owners and managers need to start spending a good deal of time thinking about what is happening to their industry and how they will need to change their place in the media use mix. They need to seriously consider what business they are in and what unique value they produce so they can reposition their functions for audiences and advertisers.
The structure and offerings of the radio industry have been adjusted several times during its 9-decade history, but the last time the industry needed to recreate itself so dramatically occurred with the arrival of television. The arrival of television resulted in radio shifting from a general entertainment and information medium to a music entertainment platform in many nations. In the U.S., broadcasters on A.M. radio later shifted toward a talk and sports platform after F.M. developed and music migrated to that spectrum, creating new opportunities on both bands.
Repositioning radio again will not be a simple task, but it is one the industry needs to begin undertaking now. If radio managers do not start thinking ahead about the negative trends appearing in their industry, they will soon experience the alarm and fear that is pervasive in the newspaper industry. It is better for companies and industries to act before crises develop fully because they can respond to and help direct the course of change rather than merely experience its negative effects. Whether decisive action will emerge in the radio industry before we reach that point remains to be seen.
International Business Information
I am interested in the import/export business. I only what to be an agent, at this time. I would like to know if I locate the buyer, where do I get help to close the deal and make a fee for my efforts.
I have been to export/import site's I have a lot of this information from export.gov and us export.gov
This information is helpful but you can have all the information in the world if you don't know the steps to process.. it's no good. I have plenty of contacts; I have done my home work. I was told that the freight and banking information is important and the freight companies part, helps with the paper work.. send me information. I have a lot of the information already, that's where I started!
I am looking for your help to refine the process. as I am more detailed oriented.
What is our first step? etc... I have a list of manufactures etc... I want to do a deal. as an agent 1st then move up the latter. So what ever product I can move as an agent, without the licensing part, (at this time) I'm in. I have a list of buyers also. but we need to know the preliminaries; evaluate opportunities, product , shipping, country, pricing, etc..
Import Export Business Answer:
I understand exactly where you are at - I was there 20 years ago - I
only wish the Import Export Toolkit self study course we offer had
been available then as we make it available now - see details here:
Starting An Import Export Business
The course provides you with the step by step you are seeking - yes,
some of it may be redundant to what you already know, but if you are
seeking step by step, then the toolkit is your best resource.
This person never followed our advice in getting a comprehensive self-study course and about two weeks later emailed us again with the following request:
Follow Up Question:
i have a diamond deal i would like so help on
Our Answer:
Sorry cannot help you on this one except to say, BE VERY CAREFUL.
Most diamond sales are locked up through the big diamond buying companies and
this is very much a closed market just as Oil, Urea, Sugar, Precious Metals, etc..
These type of deals are generally foisted on those who have little or no knowledge of
the import export business but who have a lot of interest in getting rich quickly and easily - sorry, there just is no such thing in this industry or any for that fact.
FOLLOW UP COMMENTS:
The above exchanges illustrate what I call "Blinded By The Hype". This person does not view the import export business as a business, but views it as his lottery ticket where he can make a quick score and sit back drinking margaritas on a beach somewhere for the rest of his life.
Literally, he would be better off buying lottery tickets because he is not serious about going into business and at least when he buys a lottery ticket, he really does have a chance of winning something as opposed to losing everything he owns and maybe more if he follows the yellow brick hype path that he apparently is doing.
Comments, criticisms, suggestions are always welcomed!
Ron Coble
Coble International Marketing Services
http://www.importexporthelp.com/
THE TRANSACTION COST PROBLEM OF NEWSPAPER MICROPAYMENTS
To create the best industry wide effects, a micropayment payment system would need to include as many papers as possible (see "The Challenges of Online News Micropayments and Subscriptions" http://themediabusiness.blogspot.com/2009/05/challenges-of-online-news-micropayments.html). The fact that a consortium is currently being sought only among the major players illustrates, however, that such a system would be cost inefficient because content from smaller papers would attract fewer transactions and be more expensive to service.
A widely inclusive system would encounter the problems of small payouts that have plagued collecting rights societies for authors, composers, and performers. Those systems have found that the costs of managing transactions, accounting and auditing, and conveying funds to rights holders incur higher expenses than the payments due many rights holders and that such a system is possible only when the rights holders and content that generate the most transactions subsidize those that generate the least.
This occurs because each right must have a separate account, uses of all rights must be monitored and recorded, funds must be collected, expenses for accounting, auditing and other administrative costs paid, and funds must be transferred to recipients. These activities incur significant transaction costs.
Even a cooperative system limited to newspapers that attract the largest number of customers will encounter transaction cost challenges.
In single content sales systems, for example, the cost of making transactions takes up the bulk of the price. In the sale of mobile telephone ringtones, for example, the composer, arranger, and performer get only about 20% of the price. For digital song downloads everyone associated with the content--songwriter, arranger performers, and record company--receive less than half. This occurs because merchant and financial transaction costs are very high. The cost for using a credit card adds 5 to 7 percent to merchant costs and the expense for bank processing of each transaction is a minimum of about 25 cents. Even electronic fund transfers between bank accounts incurs about 30 cents in transaction costs.
These realities will affect the structure and pricing of newspaper article micropayment purchases. The most efficient system for users and firms will require the use of prepaid customer accounts to reduce the number of bank system transactions. This will allow users to transfer funds to their accounts and then purchase articles at pennies a piece. Funds collected would be then periodically transferred to papers. Such a system could also include the option for occasional users to make credit cards purchases of articles, but the price would have to be $2 to $10 per article to make it worth the effort.
The biggest pricing challenge, however, is that some articles will be more valuable than others and will be most sought after by consumers. This means newspapers will have to figure out BEFOREHAND which stories fall into those categories and they will have to decide what prices to charge for them. Papers will have to hire personnel to try to figure out before publication which are the most economically valuable stories--something that will be extremely hard to do--or they will have to set prices based on the costs invested in creating each story (something current newspaper accounting systems do not support). In either case, increased costs will result. The only other reasonable option is to set prices per article based on the overall average cost of producing an article or a column inch of editorial copy. This, of course, over and under prices content simultaneously.
Moving to a micropayment system is not merely a matter of starting to charge for content online, but involves changing the fundamental business model of papers. Newspapers have historically bundled all content into one product available at a single price. In retailing, bundling has always worked best for getting consumers to buy more of the product at a lower price than if bought individually. With this tactic the producer gains profit because the costs of distribution and sales are collectively lower. A second tactic involves bundling products of unequal or uneven value that are sold together to achieve a joint price that is higher than would have been obtained individually.
Newspapers have historically benefited from such bundling by filling pages with relatively inexpensive news agency and syndicated content and by including huge amounts of information culled from public sources that did not require significant investment of resources or added value. Unbundling and selling individual articles with a micropayment system will produce little consumer willingness to pay for this type of content--a significant problem because it is the bulk of editorial content in most newspapers today. Unbundling will also increase transaction costs, thus reducing profitability. This will force higher prices on consumers that will affect demand.
Disaggregating the newspaper and making more money off some individual articles will also create pressure for additional payments from journalists who write the most valuable articles. This will also increase costs of the micropayment system.
Making money from online journalism is, thus, not just a matter of saying "Let's all start charging." It will require fundamental rethinking of the value chain, what content is offered, and how it is produced. It will also require significant thought about what's in it for consumers--something that is glaringly missing from current discussions of starting online payments. The consumer challenge is especially salient because most online news readers do not currently buy newspapers. If they are not willing to pay for news in print, why will they suddenly be willing to pay for that same news online? If papers can't figure that out, no decision to implement micropayments will end happily.
GOOGLE SETTLEMENT STEALS RIGHTS AND REWARDS APPROPRIATION
The settlement has been supported by the Association of American Publishers—which represents major publishers—because it protects their interests, but it is opposed by the National Writers Union and the American Society of Journalists and Authors because it seriously degrades the rights and interests of those who actually write the content. The split between publishers and authors is not surprising because anyone who has observed the uneasy relationships between musicians, authors, scriptwriters and recording, publishing, and production companies immediate recognizes they have very different and competing interests.
Under the proposed settlement, the court will take away portions of my copyrights that were created under legislation and protected by international treaties and it will give them to Google. The only way for me to protect my rights is to take deliberate affirmative action to opt out of the settlement and to seek to enforce my rights against Google individually—not a great option since its capacity to hire lawyers and stretch out litigation is far higher than mine.
The process and effects of the settlement are stunning and will dramatically alter authors’ rights. For nearly a hundred and fifty years copyright law has recognized that copyrights belong solely to the author (or persons to which the authors sell them) and that commercial uses of copyright material can only be made through negotiating terms of use and payment with the copyright owners.
The Google settlement will essentially rewrite copyright law by allowing the company to use the material without permission, without negotiating how the material will be used, and without negotiating compensation and payment provisions. It is particularly offensive because the court will be saying the government doesn’t have to protect authors’ rights, but authors’ have to protect their own rights. This is a significantly different approach from that which prosecutors and courts have taken in the cases of music, game, and software file sharers who have violated copyright on the Internet.
The settlement disassembles the basics of copyright law without legislative consideration and essentially forces the results on rights holders. Its effects are far reaching. Not only does the settlement apply to U.S. authors, but it is binding to authors worldwide even if they are not aware their rights are affected by the suit.
The settlement turns copyright upside down. Instead of protecting authors’ rights, the proposed settlement asks the court to reallocate the economic and moral rights to authors’ work, to give Google rights to use their material, and to determine the compensation authors must accept. To make matters worse, the effect of the settlement essentially gives Google a monopoly over the scanned publications and does require the company to make them available to other online services that might offer them at different prices or with different compensation for authors.
The proposed settlement is theft—pure and simple—and its proponents want to ravage and rewrite authors rights so that Google's acts will no longer be defined as larceny. The result will reward Google for illegally appropriating material, hardly a message that society should want to send to thiefs.
If the court accepts the settlement, authors will be victimized for the sake a $150 billion Internet company and the world’s biggest publishers. Where is the equity and the justice?
JOURNALISM STARTUPS ARE HELPFUL, BUT NO PANACEA FOR NEWS PROBLEMS
These initiatives should be lauded and supported. However, we have to be careful that the optimism and idealism surrounding these efforts not be imbued with naïveté and unbridled expectation. All these initiatives face significant challenges that require pragmatism in their organization and sober reflection about their potential to solve the fundamental problems in the news industry today.
We need to recognize that these online initiatives are not without precedent. We can learn a great deal about their potential from other community- and public affairs-oriented media endeavors. Community radio, local public service radio and television, public access television, and not-for-profit news and public affairs magazines have existed for decades and provide some evidence about the potential of the startups. Most rely heavily on the same types of foundation, community support, and membership financial models that startups are employing and this gives them a head start in the competition of those resources.
Despite sharing fundamental objectives and goals, these existing news and public affairs enterprises exhibit wide differences in the services they provide and their effectiveness in offering them. Many suffer from precarious financial conditions.
For the most part, such initiatives are highly dependent upon volunteer labor, individuals with the best of intentions who contribute time and effort. Those who manage the operations must expend a great deal of effort to train, coordinate, motivate and support these volunteers. This incurs cost and takes time from other activities.
Most of the organizations operate with highly limited staffs of regularly employed personnel and this is especially true in news operations. Professional journalists working in these organizations tend to be poorly paid; few have health and retirement benefits; most do not have libel insurance that protects aggressive and investigative reporting; few have access to resources to invest time and money in significant journalistic research. The consequence of these challenges is that there tends to be high turnover because the operations typically rely on young journalists who use the organizations to gain professional experience and then move on to better funded or commercial firms.
The community and public affairs operations also exhibit widely disparate size and quality in their journalistic activities. Even most affiliates of National Public Radio—which is generally considered the most successful of non-commercial news operations—tend to have small and relatively undistinguished news operations. Most rely upon the exceptional content of the national organization, large metropolitan affiliates, and the best of the content collectively produced by other local affiliates. Affiliates with larger news staffs and quality tend to be limited to those linked to university journalism programs or in the best-funded metropolitan operations.
The challenges faced in these organizations should not deter the establishment of new online initiatives or keep the rest of us from supporting them. We need to be realistic about their potential, however. In the foreseeable future these startups will tend to supplement rather than to replace traditional news organizations. They may be part of the solution to the problem of news provision, but they alone are not the remedy.
OMG! NEWSPAPERS MAY NOT BE DEAD!
To be successful an enterprise must offer a product or service that people want; it must provide it with better quality and service than other providers—or at a lower price than competitors; it must change with the times and demand; and it must never forget to focus on customer needs rather than its own. And a limited number of competitors helps. Duh.
Many journalists have trouble understanding these principles, however, and we were treated to 2 classic stories in which journalists breathlessly announced this discovery over the weekend.
The New York Times told us about the “resurgent” Seattle Times. The Times is starting to reap the fruits of monopoly caused by the demise of the print edition of the Post-Intelligencer and the stabilizing economy. It has picked up most of the print readers from the P-I, raised its circulation prices, and been able to keep the higher ad rates that were charged when ads were put in both papers. http://www.nytimes.com/2009/08/10/business/media/10seattle.html
The Associated Press told us “Small is beautiful” and that local papers do not feel competition for big players like CNN, metropolitan television, and Craigslist because they focus on local news and advertising not available elsewhere. “Less competition means the print editions and Web sites of smaller newspapers remain the focal points for finding out what's happening in their coverage areas.” http://tech.yahoo.com/news/ap/20090809/ap_on_hi_te/us_small_newspapers_1
Journalists are also starting to discover that the industry might not be as dead as they have been portraying it to be. A number of stories have reported that the drop in advertising due to the recession appears to be near bottom, that profits and share prices are rising, and there is no wholesale rush to the web by print newspaper readers.
These “surprises” are developing, I believe, because journalists have never covered their own industry with the same interest and vigor that they have covered other industries. This is partly true because they have adamantly and publicly expressed distain for the business side of the news industry and because they tend to accept and endlessly repeat the views of publishers without critical fact checking or seeking better understanding of the business dynamics of news. Whatever happened to the old journalism adage "If your mother says she loves you, check it out!"
Perhaps they will learn.
PROFITS, RECESSION, AND RECOVERY
The developments must come as a surprise to those who saw the poor performance of recent quarters and convinced themselves that the newspaper industry is dead and gone.
Admittedly, the positive results in the past 3 months were achieved through restructuring, reducing news staffs to their 1970s levels, heavy cost cutting everywhere, and postponing reinvestments. But it shows there is still life in the industry and that the industry can be expected to recover in the coming year if economic conditions continue their current rate of improvement. As I have said many times, a industry with $50 billion in revenue is not going to ignore that revenue, close the doors, and disappear overnight.
Many have viewed the poor company performance in the past 2 years and then mistaken the steep concurrent drop in advertising as evidence of a general decline caused by long-term industry trends. In doing so, they have disregarded the impact of the economy on newspaper advertising and mistaken the dramatic drop in advertising as being an indicator of the industry's broader condition rather than the shorter-term results of 4 quarters of negative growth that have affected the economy as a whole. Some have also ignored the effects of corporate debt problems had on the industry's overall condition.
In multiple blogs and articles journalists and editors have pointed out that newspapers have fared worse than other media in the recession and used that the fact as evidence that the industry is a death's door. Two decades of research on newspapers during recessions, however, has shown newspapers typically fare worse because retail and classified advertising on which the industry relies are more affected by downturns than brand advertising (See post “The Credit Crisis, Volatile Markets, and Recession and Media” and the articles below). Obviously a lot of newspaper managers and journalists don't pay attention to research about their own business.
If one looks at the newspaper advertising expenditures over time (see Figure below), one sees that they fall with recessions and then recover. This pattern was especially evident from 1991 to 1993 and 2001-2003 when short downturns pushed newspapers into decline.
 If one considers different category of advertising, it is clear that the classified advertising—which was a driver of growth in the 1990s—was significantly troubled after 2000, but recovered and spiked in 2005 (Figure 2). Its relative decline by comparison to retail and national advertising is probably the result of some substitution with the Internet, nevertheless newspaper classifieds produced $10 billion in 2008—3 times that of online classified.
If one considers different category of advertising, it is clear that the classified advertising—which was a driver of growth in the 1990s—was significantly troubled after 2000, but recovered and spiked in 2005 (Figure 2). Its relative decline by comparison to retail and national advertising is probably the result of some substitution with the Internet, nevertheless newspaper classifieds produced $10 billion in 2008—3 times that of online classified.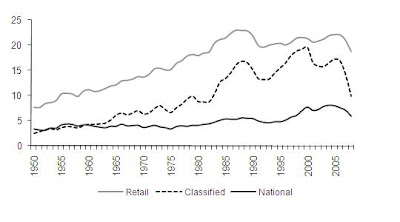 U.S. newspapers are in a mature industry with low growth potential once recovery from the recession occurs. Most companies will performance reasonably well after the recovery, but certainly some companies will have difficulties because of imprudent strategies and choices. Nevertheless, the industry as a whole will still remain in place producing revenue for many years to come.
U.S. newspapers are in a mature industry with low growth potential once recovery from the recession occurs. Most companies will performance reasonably well after the recovery, but certainly some companies will have difficulties because of imprudent strategies and choices. Nevertheless, the industry as a whole will still remain in place producing revenue for many years to come. Picard, R.G. (2001). Effects of Recessions on Advertising Expenditures: An Exploratory Study of Economic Downturns in Nine Developed Nations, Journal of Media Economics, 14(1): 1-14.
100th Post - Import Export Business - Is It Really For You?
This is the 100th post to this blog - I am baring my soul (so to speak) as to why an international business offers import export training courses - I hope this post will help you make the final decision as to whether import export is for you or isn't and why it is important to make INFORMED decisions, both before, during and after starting your business.
In the learning phase of my own business in the late 1980's, I did not have the HUGE advantage that the Internet offers you. I had to make innumerable visits to the library which was about a 20 mile round trip.
I spent hundreds of hours there researching, reading, copying. I spent hundreds of dollars on training materials that were extremely outdated (that was the 80's and the materials were written in the 60's and 70's). I wasted thousands of dollars on postage sending inquiries to trade leads that were so outdated it was almost enough to make you want to quit.
I visited with international bankers, department of commerce personnel, actual live importers and exporters to gather as much information as I possibly could.
Because of all the expenses of trying to learn this business piece meal, an idea came upon me one day that some people might be interested enough to pay for reports that compiled all this research into a current newsletter and thus the information part of my business was born.
The newsletter drew the attention of a publisher in Washington DC (at the time) who published a newspaper filled with trade leads each month. I agreed to sell his newspaper along with our newsletter after I tested the leads.
The first lead was for Organic Fruit Juice. Although the lead was about 2 months old I called the buyer and he advised me that only one other person had contacted him. He was definitely still interested and asked for quotes.
Off to the library, I researched and found 6 companies that produced it. I contacted 5 and was rejected - they were not interested. The sixth and last was. I had to pay a local machine shop a dollar a page to send and receive each page of a fax (this was 1988 remember).
I faxed an agreement to the producer after we agreed to terms by phone, they signed and faxed the agreement back and I then put the two parties together. Only two sales ever resulted from that deal but I was paid approximately $1,000 for about 3 hours of work/research.
This does not mean you will make that much on your first deal or that little, it is presently purely to document our first export deal.
Our business evolved and about 1993 we were contacted by a publisher of an import and export business course. After having such a bad experience with those I had purchased, I wanted to review it before agreeing to sell it (this was ll by mail order at the time).
I was thoroughly impressed with both the course and with the publisher. Since 1993 we have been offered the chance to market just about every other export/import course there is on the market and after reviewing them, nothing comes remotely close to the vast amount of information presented in such a manner that it is easily understood.
Because of our experience in the industry, our publisher has implemented many of the suggestions that we provided. Many of the questions and answers that were received during these 16 years have been included in the updates made to the course materials which averages about every 2 years.
Quite frankly, the revenue from the sale of these courses only represents about 5% of our total annual revenue and if it were to end tomorrow, it would hurt but it could easily be replaced with other revenue streams.
So why do we continue to offer the courses? Several reasons:
- There are many people out there who are like I was 21 years ago - people who have a sincere interest in the international trade business but do not know how to go about getting it in a manner that is easy to understand and not go broke or spend hundreds of hours like I did.
- There has been a proliferation of offerings that are out there with the advent of the Internet - some ranging from as little as $10 to others ranging $8,000 or more and I know in my heart that the courses we offer are the BEST based on my personal review and 21 years experience.
- Many of the people described above will end up calling or emailing me and rather than taking trying to explain the same processes over and over and over, they have a comprehensive course that is not only training but a resource library for the entire term of their business.
- There has to be training available that is not too complicated like many courses are that will discourage you before you ever take the first step and a course that is not so outlandish in price that you have to take a 2nd mortgage (if you can get one) for the promises of some boiler room operator/trainer who has absolutely no real life experience in this business and in my 21+ years of experience I have yet to find any course that is better - if I did, it would be posted to our web site tomorrow.
The Import Export Business is just that - A business! It is NOT an OPPORTUNITY that will magically transform you into a super worldwide success. This is a REAL business that without the serious application of WORK by YOU will not provide you with anything by and of itself!
This business is NOT for everyone (bet the boiler room operators whose weekly commission check depend solely upon selling you their $8000 plus 'program' will never tell you that)!
Here is a list of people who will have a problem succeeding in this business:
- Those who cannot write a sentence or paragraph in basic English (sorry but English is the main language of international trade).
- Those who will not pick up the phone and call someone and be able to speak English well enough that the other party can understand them - if the truth offends you, then I have save you from a lot of wasted money and time.
- Those who need a coach or camp counselor who they can call and cry on their shoulders when they cannot get a buyer or seller to talk with them - when in reality the camp counselor/coaches by the $8000+ programs are nothing more than boiler room operators with the same printed material in front of them as you have in front of you - this is all part of business - the buyer or sellers in the world are not waiting for you with baited breath so you can tell them about the "certificate" you now possess as if that really means anything in this industry.
- Those who are unable to make a decision for themselves even after they have been provided with all the details and processes that are necessary for them to make an informed decision - they are not ready to be in business for themselves, they need a job where they have a boss who will tell them what to do for 8 hours.
- Those who think an exorbitant price somehow translates into something being better - they think well if it costs that much, it must be good, right?
- Those who are too lazy to perform due diligence (read our company page for instructions) - if you are going to invest $8,000+ in the belief a company is what they say they are, spend a couple of hundred and fly out to their location, see their "warehouses" (I find it amusing that some people expend more time checking us out for an investment in a course that is less than 5% of the $8K+ program)
- Those who, even after they perform 'in-depth' due diligence, still foolishly throw their $8K+ at a dream that is sold to them by a commissioned salesman/woman with absolutely no experience in the industry.
I wish everyone who purchases a course from us would be an incredible success, but the sad fact is probably less than 5% ever follow through and take the first step of action necessary to achieve any success.
If you think the $8K+ programs offer you a better chance, give me a call during normal business hours at 717-292-5763 - if I am in the office I will gladly tell you how to do a very simple google search to find the thousands of now inactive web sites that others who have taken the $8K+ path have followed. I just did this search today and quite frankly I was amazed at how many there are but before you call me - DO YOUR OWN DUE DILIGENCE and if you are really cut out to be in business for yourself, you will not need to bother calling me because you will have already made the right decision.
The courses we offer will provide you with everything, step-by-step instructions on how to succeed in both importing and exporting - the success factor is what looks you in the mirror each morning.
If any of the above has offended you, well let's say in this area of Pennsylvania, we have an old saying the goes "if the shoe fits, wear it!" If it took this as a slap up along the side of you head and you are offended and you forget about this business all together, then I have accomplished my goal as you simply are not ready for this business.
If however, you are the type of person who says, great, finally someone who tells it like it is, no bull shit, someone who not only talks the talk but who has walked the walk, well then you are ready for our course and for being in business for yourself (as long as you can handle the oral and written communications).
Bottom line, we offer the courses we do because our experience tells us that they are the best - we could earn 10 times what we do if we opted to sell the $8K+ program (and believe me they would love to get exposure to our 53,000 monthly visitors) but quite frankly, I would rather lose that 5% of income and not replace it with anything if their program was the only choice available. That would free up more time for me to spend with our rapidly growing grand child.
That is it for my 100th post to this blog - I hope you have found it to be both helpful and enlightening, comments, criticisms are "always" welcome (you do have to register with blogger.com to comment, however).
Thanks for visiting and taking the time to read what I hope is one of, if not the most, thought provoking post since we began this blog.
Ron Coble
ONLINE AGGREGATORS AND NEWSPAPER STRATEGY
Aggregators carry news stories from major news services and thus make international and national public affairs, entertainment and sports news widely available. The headline news on the aggregators’ home pages is becoming the primary news provider for those less interested in news and the online sections are well-used by news consumers who want more news or more timely news than appears in their daily newspaper.
Aggregators and others sites carrying content from news services are now contributing about 20 percent of the revenue of Associated Press, for example, taking some financial pressure off newspapers to fund the cooperative on their own. Other news services are also gaining income from online operators, thus helping them keep prices lower for newspapers as well.
So how do aggregators news harm newspapers? They harms papers to the extent that some less committed newspaper readers are willing to substitute their local paper with a news sources that don’t cover their cities. Some are willing to do so and this is taking some subscribers and single copy purchasers away from newspapers. U.S. newspapers have lost approximately 6 million circulation since 2000, but about half of that was circulation of the 70 competing newspapers or second editions papers that have been closed since the millennium. So one can thus say that at least 3 million people have decided to use other news sources.
Aggregators are also accused of STEALING value through their search functions and links to newspaper sites. Certainly the aggregators are CREATING value with the technique but are they taking value in violation of copyright or norms of content use? The answer is “no” because they do not represent the material as their own and direct those searching to the newspapers own sites, where they are exposed to advertising sold by the online newspapers.
Newspapers are now getting between 7-10 readers online for every reader they have in print. This plays an important role in making their sites attractive to advertisers, a development that generated the $3.2 billion in online advertising revenue that newspapers received in 2008.
Newspapers, of course, could stop the aggregators from linking to their content by putting it behind walls and charging for its use. If they did so, the aggregators could not link to it legally or technically without users encountering a pay or registration wall. So why haven’t newspapers done this until now? Frankly, because they get more readers and more advertising income by offering the material free.
Publishers are increasingly arguing that they should turn newspaper sites into paying sites and they have been holding joint discussion about how that might happen and whether it would be beneficial to do so simultaneously. This has raised some antitrust concern, but it raises real and significant questions of what such a strategy would accomplish.
In my estimation it is not as easy answer to the challenges newspapers face and has some elements that put its effectiveness in doubt. This is primarily because it is uncertain what existing readers will do. Will they subscribe to print AND online? Will they stay with print only? Or will they drop print?
The first option would be financially beneficial, but is likely to attract a limited number of readers unless the joint pricing is so attractive that it produces little new income for the newspaper firm. If that is the case the benefit of the strategy is reduced. The latter option would be very damaging to papers because print advertising creates more value than online advertising and prices for print ads would decline more than would be gained online.
It also needs to be recognized that people who do not currently buying newspapers are unlikely to buy subscriptions to online news sites. Thus, creating a paid model will likely reduce the boosted audience that free online news currently provides. This would have a negative effect on online audience and the increasing revenue that is being obtained from online advertising.
But what of heavy news users? As I have written in other entries in this blog, heavy users tend to be promiscuous and move between many online news sites. A commonly used system for micropayments would be necessary or these heavy users will reduce their use of multiple sites if each requires separate payment registration. Even with such a system in place, it is unlikely that more than 5-10 percent of the newspaper purchasing population would regularly use such a system.
Moving to a paid online model will not be as easy as agreeing that everyone should switch to paid on January 1 next year. It will require considerable strategic thinking and providing new types of value for consumers if it is to be successful. Even then, the benefits for newspapers will vary significantly depending upon the size, location, and competitive situation of individual newspapers.
THE POOR CONNECTION BETWEEN INTERNET ADVERTISING AND NEWSPAPER WOES
There is no question that Internet is increasingly attracting advertising revenues. They reached $23.4 billion in the U.S. in 2008. Looking at the numbers more closely, however, one sees a different story. About half those expenditures are search and lead generation fees that don’t compete with traditional newspaper advertising. Search payments alone are the single largest category of Internet income and represent 40% of total online fees.
Internet classified advertising—the direct competitor to newspaper classifieds—has never exceeded 20 percent of online advertising revenues and it is declining as a percentage of the total. Online classified advertising was $3.2 billion in 2008, about one third of the classified advertising expenditures in U.S. newspapers. Nevertheless, some newspaper executives and industry observers act as if all the online classified revenue has been diverted from newspapers, but the evidence of that is not very persuasive. As this figure shows, between 2003 and 2006, Internet classified grew considerably, but newspaper classifieds not only held their own but increased as well. Clearly there has been a significant decline in the past 2 recession years, but there is no evidence it is shifting to online classified advertising.
U.S. NEWSPAPER AND ONLINE CLASSIFIED EXPENDITURES, $ BILLIONS
 If one considers annual gain or loss of classified advertising in the two media one sees that the patterns do not indicate any substantial demand side substitution (advertisers switching from one to the other) because the figures do not rise and fall in the same patterns or in somewhat similar amounts.
If one considers annual gain or loss of classified advertising in the two media one sees that the patterns do not indicate any substantial demand side substitution (advertisers switching from one to the other) because the figures do not rise and fall in the same patterns or in somewhat similar amounts.NET GAIN/LOSS FOR NEWSPAPER AND ONLINE CLASSIFIEDS, $BILLION
 So why does the Internet constantly get the blame for newspaper woes? I believe it is because of it is just the newest in a series of threats to newspaper revenue. The Internet certainly is taking some money from newspapers, but it isn’t the worst culprit. The real competitor is direct mail and home delivery advertising that have taken much preprint and display advertising from newspapers in recent decades by delivering better household reach. That was compounded by the significant reduction in the number of large retailers in the late 1990s and 2000s. The development of the recession in 2007 and 2008 is currently playing the major role because newspaper advertising—especially classifieds—is more strongly affected by recessions than other types of advertising. But recessions come and go and there is no reason to believe that an advertising recovery will not accompany an improvement in the economy.
So why does the Internet constantly get the blame for newspaper woes? I believe it is because of it is just the newest in a series of threats to newspaper revenue. The Internet certainly is taking some money from newspapers, but it isn’t the worst culprit. The real competitor is direct mail and home delivery advertising that have taken much preprint and display advertising from newspapers in recent decades by delivering better household reach. That was compounded by the significant reduction in the number of large retailers in the late 1990s and 2000s. The development of the recession in 2007 and 2008 is currently playing the major role because newspaper advertising—especially classifieds—is more strongly affected by recessions than other types of advertising. But recessions come and go and there is no reason to believe that an advertising recovery will not accompany an improvement in the economy.I don't mean to say that some former classified advertisers are not shifting to online sites, or starting their own company sites, allowing allows them to market more inexpensively. But newspapers can strive to get them back and to keep others from leaving by aggressively marketing to those people and firms and by creating effective print and online newspaper classified packages that provide more effective advertising responses for them.
The end for newspapers is not in sight and those who think that the $50 billion industry is going to collapse and disappear within a year or two because of Internet advertising are just not paying attention close enough attention to what is really happening across media industries.
Web Wholesaler - New Product & Merchandise Sources

Web Wholesaler offers the latest in new products and merchandise sources, ideas and statistics on what is selling online NOW, as well as up to the minute news and information on industry trends, e-business growth and management strategies, and methods for increasing your revenues.
- Web Wholesaler is complimentary to qualified professionals
- Geographic Eligibility: USA
- The publisher determines qualification and reserves the right to limit the number of free subscriptions
- Offered Free by: Sumner Communications
SALARIES RISE BUT JOURNALISTS DON'T BENEFIT
According to the salary study, average newspaper wages in the U.S. increased 2.1% between 2008 and 2009, but that result was skewed because hefty increases went to producers of interactive (online) content and editorial personnel involved in new business development. Journalists on the average received no or marginal increases depending upon their category.
My lecture, which was carried in a significantly reduced form in the Christian Science Monitor , and redistributed by multiple online sites and blogs, produced shock, anger, and invective by many journalists who missed its point. The text of the full lecture can be found at the website: http://www.robertpicard.net/files/Why_journalists_deserve_low_pay.pdf
Journalists today create very little economic value and are having a difficult time getting people to pay for the social value they create. The fact that newspapers are rewarding those who help create new businesses and revenue streams far above traditional journalists accentuates this point.
I admit that the title of my speech was deliberately provocative. It was meant as a wakeup call from a former journalist who loves the news industry. The reality is that no one deserves either high or low pay. The level of pay is EARNED. Journalists deserve pay based on the economic value they create (evidenced by what the public is willing to pay for news) or on the willingness of the public to support social purposes contributing funds to foundations or non-profit news operations.
In today’s world—in which the mass audience for newspapers and its business model are disappearing—continuing to provide the same types of coverage and content in the past will not create economic value and earn good pay. I do not believe that Internet news aggregators, community journalism, and blogging will ever replace the functions of good journalism and it will not replace the functions of most newspapers in the short to mid-term. There is hope for journalism.
If journalists want to promote good journalism and value creation that makes them earn more pay, they will have to take more responsibility for coverage decisions and content choices so that journalism becomes more valuable. Journalists have shown unusual willingness to leave those decisions to publishers and editors who have stopped acting like journalists. But it need not be that way.
THE END OF JOURNALISM?
Many of the voices and opinions, however, misunderstand the nature of journalism. It is not business model; it is not a job; it is not a company; it is not an industry; it is not a form of media; it is not a distribution platform.
Instead, journalism is an activity. It is a body of practices by which information and knowledge is gathered, processed, and conveyed. The practices are influenced by the form of media and distribution platform, of course, as well as by financial arrangements that support the journalism. But one should not equate the two.
The pessimistic view of the future of journalism is based in a conceptualization of journalism as static, with enduring processes, unchanging practices, and permanent firms and distribution mechanisms. In reality, however, it has constantly evolved to fit the parameters and constraints of media, companies, and distribution platforms.
In its first centuries journalism was practiced by printers, part-time writers, political figures, and educated persons who acted as correspondents—not by professional journalists as we know them today. In the nineteenth century the pyramid form of journalism story construction developed so stories could be cut to meet telegraph limits and production personnel could easily cut the length of stories after reporters and editors left their newspaper buildings. Professionalism in the early 20th century emerged with the regularization of journalistic employment and professional journalistic best practices developed. The appearance of radio news brought with it new processes and practices, including “rip and read” from the news agencies teletypes and personal commentary. TV news brought a heavy reliance on short, visual news and 24hour cable channels created practices emphasizing flow-of-events news and heavy repetition.
Journalistic processes and practices have thus never remained fixed, but journalism has endured by changing to meet the requirements of the particular forms in which it has been conveyed and by adjusting to resources provided by the business arrangements surrounding them.
Journalism may not be what it was a decade ago—or in some earlier supposedly golden age—but that does not mean its demise is near. Companies and media may disappear or be replaced by others, but journalism will adapt and continue.
It will adapt not because it is wedded to a particular medium or because it provides employment and profits, but because its functions are significant for society. The question facing us today is not whether journalism is at its end, but what manifestation it will take next. The challenges facing us are to find mechanisms to finance journalistic activity and to support effective platforms and distribution mechanisms through which its information can be conveyed.
Gardening Equipment Supply Importers
If your company or any of the companies you represent manufacture lawna and/or garden equipment, supplies or furniture, then you need to review details of this commodity specific trade directory that provides you with details on over 4,000 garden equipment importers, lawn equipment importers, gardening supplies importers and patio equipment importers from 143 different countries who import garden equipment, lawn equipment, gardening supplies, plants, trees, agricultural chemicals, garden chemicals, irrigation equipment, spraying equipment, greenhouses, patio furniture, outdoor lighting, and tractors. Just follow the link below:
Lawn And Garden Equipment - Furniture and Supply Importers
Now for any of you folks who are into gardening and would like to read all that you can about garden plants, garden supplies and general gardening information, I would like to personally recommend that you check out this web site for all your Gardening Tips - Plants and Supplies
Have a Great Weekend!
The Challenges of Online News Micropayments and Subscriptions
In recent weeks Rupert Murdoch announced News Corp. will begin shifting its newspapers to an online paid model in the next 12 months, starting with Wall Street Journal and then progressively shifting papers such as the New York Post, The Times of London, the Sun and The Australian to a paid model. Dean Singleton followed by indicating MediaNews Group will begin doing the same for its papers, including Denver Post, San Jose Mercury News, Detroit News, St. Paul Pioneer Press, and Salt Lake city Tribune.
Clearly charging for online news is likely to reduce online consumption because of elasticity of demand, but—setting aside the extent to which demand for online news will fall if a price is imposed—moving to a paid model will also creates two common, industrywide challenges.
First, it forces each publisher to bear costs of setting up their own payment system. Secondly, it imposes a heavy burden on consumers. The latter burden results not from having to pay for news, but from the fact that online readers typically do not use only one online news source—unlike the market for print newspapers in which readers typically subscribe to only one paper.
It currently appears that each online newspaper or their corporate parent will set up their own payment systems. The options being most discussed are subscriptions for use or electronic wallets from which to make micropayments for occasional use.
These factors will have a particularly negative affect on the heaviest online news users—voracious and promiscuous readers who seek news from multiple news organizations. If each newspaper sets up its own payment system, for example, these readers will have to have separate payment accounts for the New York Times, Washington Post, Los Angeles Times, Wall Street Journal, The Guardian, and dozens of other publications they wish to visit.
To deal with this challenge the newspaper industry should seek to create a joint venture or cooperative to solve the problem. Companies should work together to developing a single system that is usable across sites and one that can be extended to handle payments for other types of online content. Such a system would simplify and encourage payment for content, but also develop a new revenue stream by turning the payment system from a cost center to profit center by charging companies for its use.
Free is clearly not the right price for news, but the movement to a paid model will not be as simple as transferring the existing subscription and single copy payment models for print newspapers to their online counterparts. Seeking payment online creates new challenges and opportunities that will require new thinking about how payments are made and more cooperation across the industry.